Установка OpenConnect сервера в СentOS 7

Приветствую Вас, уважаемые читатели. Сегодня статья: "Установка OpenConnect сервера в СentOS 7". Произведём установку и настройку OpenConnect сервера, а так же проверим работу клиентского приложения под ОС Windows.
OpenConnect сервер – это бесплатный аналог другого продукта, под названием Cisco AnyConnect. OpenConnect – кроссплатформенное ПО. Клиентские приложения можно найти в Google Play и App Store. Клиент под Windows, можно найти на одном из ресурсов разработчиков.
Ссылка на сайт разработчиков: http://ocserv.gitlab.io/www/manual.html

Ссылка на проект с приложением под Windows: https://openconnect.github.io/openconnect-gui/
Установка сервера OpenConnect
- Для установки Ocserv, в системе должен быть подключен репозиторий epel-release. Если он не подключён, то подключаем его.
# yum install epel-release
- После подключения нужного репозитория, производим установку Ocserv, и необходимых утилит.
# yum install ocserv gnutls-utils
- Следующим шагом, создаём директорию, в которой будем производить манипуляции с ключами и сертификатами.
# mkdir /etc/ocserv/cert
- Заходим в созданную директорию /etc/ocserv/cert/.
# cd /etc/ocserv/cert/
- Создаём файл /etc/ocserv/cert/ca.tmpl с регистрационными данными для сертификационного центра. Регистрационные данные можно изменить на свои.
cn = "My CN" organization = "CN" serial = 1 expiration_days = -1 ca signing_key cert_signing_key crl_signing_key
- Выполняем команды для создания ключа ca-key.pem, и сертификата ca-cert.pem сертификационного центра.
# certtool --generate-privkey --outfile ca-key.pem # certtool --generate-self-signed --load-privkey ca-key.pem --template ca.tmpl --outfile ca-cert.pem
- Создаём файл /etc/ocserv/server.tmpl с регистрационными данными сервера. Регистрационные данные можно изменить на свои.
cn = "MY CN" dns_name = "my.cnnn" organization = "My cn" expiration_days = -1 signing_key encryption_key tls_www_server
- Выполняем команды для создания ключа server-key.pem, и сертификата server-cert.pem для VPN-сервера.
# certtool --generate-privkey --outfile server-key.pem # certtool --generate-certificate --load-privkey server-key.pem --load-ca-certificate ca-cert.pem --load-ca-privkey ca-key.pem --template /etc/ocserv/server.tmpl --outfile server-cert.pem
- Создаём директорию, в которой будут собраны ключи и сертификаты.
# mkdir /etc/ocserv/ssl/
- Возвращаемся в директорию /etc/ocserv/cert/, и копируем нужные файла в директорию /etc/ocserv/ssl/.
# cd /etc/ocserv/cert/ # cp ca-cert.pem server-key.pem server-cert.pem /etc/ocserv/ssl/
Конфигурация OpenConnect сервера
- Находим файл /etc/ocserv/ocserv.conf, этот файл отвечает за конфигурацию сервера, и производим в нём некоторые изменения.
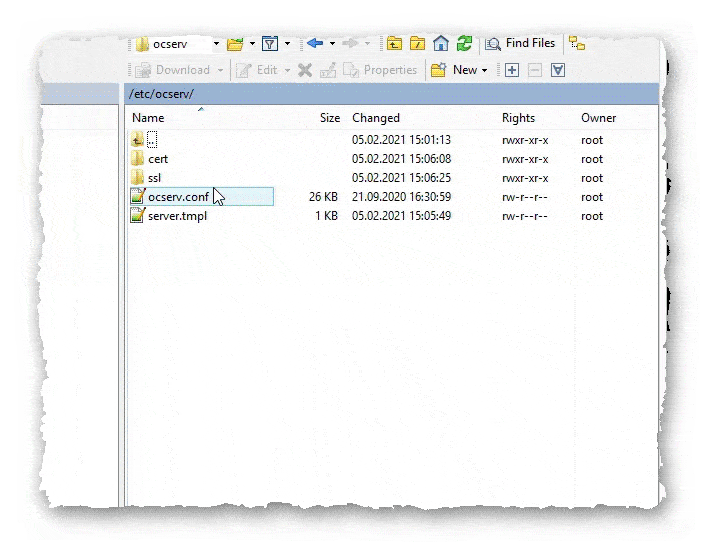
- Сначала нужно настроить аутентификацию. Для этого нам нужно отключить метод аутентификации по умолчанию, настроить свой метод аутентификации, и указать пути расположения необходимых файлов.
Закомментировать строчку auth = "pam" Раскомментировать строчку auth = "plain[passwd=/etc/ocserv/sample.passwd,otp=./sample.otp]" И заменить её на строчку auth = "plain[passwd=/etc/ocserv/passwd]" Две строчки server-cert = /etc/pki/ocserv/public/server.crt server-key = /etc/pki/ocserv/private/server.key Заменить на три строчки server-cert = /etc/ocserv/ssl/server-cert.pem server-key = /etc/ocserv/ssl/server-key.pem ca-cert = /etc/ocserv/ssl/ca-cert.pem
- Следующим шагом, укажем подсеть для нашей VPN. Для этого раскомментируем нужную строчку.
# ipv4-network = 192.168.1.0/24
- Сервер по умолчанию работает на 443 порту. Отключим режим работы по UDP, чтобы сервер был ещё менее заметен в потоке трафика.
Удаляем строчку udp-port = 443
- Напоследок - добавляем Dns-сервера в конце файла. Можете прописать какие-угодно.
dns = 8.8.8.8 dns = 4.2.2.4
- Готовый конфиг с дополнительными надстройками:
### The following directives do not change with server reload. # # User authentication method. To require multiple methods to be # used for the user to login, add multiple auth directives. The values # in the 'auth' directive are AND composed (if multiple all must # succeed). # Available options: certificate, plain, pam, radius, gssapi. # Note that authentication methods utilizing passwords cannot be # combined (e.g., the plain, pam or radius methods). # # certificate: # This indicates that all connecting users must present a certificate. # The username and user group will be then extracted from it (see # cert-user-oid and cert-group-oid). The certificate to be accepted # it must be signed by the CA certificate as specified in 'ca-cert' and # it must not be listed in the CRL, as specified by the 'crl' option. # # pam[gid-min=1000]: # This enabled PAM authentication of the user. The gid-min option is used # by auto-select-group option, in order to select the minimum valid group ID. # # plain[passwd=/etc/ocserv/ocpasswd,otp=/etc/ocserv/users.otp] # The plain option requires specifying a password file which contains # entries of the following format. # "username:groupname1,groupname2:encoded-password" # One entry must be listed per line, and 'ocpasswd' should be used # to generate password entries. The 'otp' suboption allows to specify # an oath password file to be used for one time passwords; the format of # the file is described in https://code.google.com/p/mod-authn-otp/wiki/UsersFile # # radius[config=/etc/radiusclient/radiusclient.conf,groupconfig=true,nas-identifier=name,override-interim-updates=false]: # The radius option requires specifying freeradius-client configuration # file. If the groupconfig option is set, then config-per-user will be overriden, # and all configuration will be read from radius. The 'override-interim-updates' if set to # true will ignore Acct-Interim-Interval from the server and 'stats-report-time' will be considered. # # gssapi[keytab=/etc/key.tab,require-local-user-map=true,tgt-freshness-time=900] # The gssapi option allows to use authentication methods supported by GSSAPI, # such as Kerberos tickets with ocserv. It should be best used as an alternative # to PAM (i.e., have pam in auth and gssapi in enable-auth), to allow users with # tickets and without tickets to login. The default value for require-local-user-map # is true. The 'tgt-freshness-time' if set, it would require the TGT tickets presented # to have been issued within the provided number of seconds. That option is used to # restrict logins even if the KDC provides long time TGT tickets. #auth = "pam" #auth = "pam[gid-min=1000]" auth = "plain[passwd=/etc/ocserv/passwd]" #auth = "certificate" #auth = "radius[config=/etc/radiusclient/radiusclient.conf,groupconfig=true]" # Specify alternative authentication methods that are sufficient # for authentication. That is, if set, any of the methods enabled # will be sufficient to login, irrespective of the main 'auth' entries. # When multiple options are present, they are OR composed (any of them # succeeding allows login). #enable-auth = "certificate" #enable-auth = "gssapi" #enable-auth = "gssapi[keytab=/etc/key.tab,require-local-user-map=true,tgt-freshness-time=900]" # Accounting methods available: # radius: can be combined with any authentication method, it provides # radius accounting to available users (see also stats-report-time). # # pam: can be combined with any authentication method, it provides # a validation of the connecting user's name using PAM. It is # superfluous to use this method when authentication is already # PAM. # # Only one accounting method can be specified. #acct = "radius[config=/etc/radiusclient/radiusclient.conf]" # Use listen-host to limit to specific IPs or to the IPs of a provided # hostname. #listen-host = [IP|HOSTNAME] # When the server has a dynamic DNS address (that may change), # should set that to true to ask the client to resolve again on # reconnects. #listen-host-is-dyndns = true # TCP and UDP port number tcp-port = 443 # Accept connections using a socket file. It accepts HTTP # connections (i.e., without SSL/TLS unlike its TCP counterpart), # and uses it as the primary channel. That option cannot be # combined with certificate authentication. #listen-clear-file = /var/run/ocserv-conn.socket # The user the worker processes will be run as. It should be # unique (no other services run as this user). run-as-user = ocserv run-as-group = ocserv # socket file used for IPC with occtl. You only need to set that, # if you use more than a single servers. #occtl-socket-file = /var/run/occtl.socket # socket file used for server IPC (worker-main), will be appended with .PID # It must be accessible within the chroot environment (if any), so it is best # specified relatively to the chroot directory. socket-file = ocserv.sock # The default server directory. Does not require any devices present. chroot-dir = /var/lib/ocserv ### All configuration options below this line are reloaded on a SIGHUP. ### The options above, will remain unchanged. Note however, that the ### server-cert, server-key, dh-params and ca-cert options will be reloaded ### if the provided file changes, on server reload. That allows certificate ### rotation, but requires the server key to remain the same for seamless ### operation. If the server key changes on reload, there may be connection ### failures during the reloading time. # Whether to enable seccomp/Linux namespaces worker isolation. That restricts the number of # system calls allowed to a worker process, in order to reduce damage from a # bug in the worker process. It is available on Linux systems at a performance cost. # The performance cost is roughly 2% overhead at transfer time (tested on a Linux 3.17.8). # Note however, that process isolation is restricted to the specific libc versions # the isolation was tested at. If you get random failures on worker processes, try # disabling that option and report the failures you, along with system and debugging # information at: https://gitlab.com/ocserv/ocserv/issues isolate-workers = true # A banner to be displayed on clients # banner = "Welcome to VPN" # Limit the number of clients. Unset or set to zero for unlimited. #max-clients = 1024 max-clients = 40 # Limit the number of identical clients (i.e., users connecting # multiple times). Unset or set to zero for unlimited. max-same-clients = 1 # Limit the number of client connections to one every X milliseconds # (X is the provided value). Set to zero for no limit. #rate-limit-ms = 100 # Stats report time. The number of seconds after which each # worker process will report its usage statistics (number of # bytes transferred etc). This is useful when accounting like # radius is in use. #stats-report-time = 360 # Keepalive in seconds keepalive = 300 # Dead peer detection in seconds. # Note that when the client is behind a NAT this value # needs to be short enough to prevent the NAT disassociating # his UDP session from the port number. Otherwise the client # could have his UDP connection stalled, for several minutes. dpd = 60 # Dead peer detection for mobile clients. That needs to # be higher to prevent such clients being awaken too # often by the DPD messages, and save battery. # The mobile clients are distinguished from the header # 'X-AnyConnect-Identifier-DeviceType'. mobile-dpd = 300 # If using DTLS, and no UDP traffic is received for this # many seconds, attempt to send future traffic over the TCP # connection instead, in an attempt to wake up the client # in the case that there is a NAT and the UDP translation # was deleted. If this is unset, do not attempt to use this # recovery mechanism. switch-to-tcp-timeout = 30 # MTU discovery (DPD must be enabled) try-mtu-discovery = true # The key and the certificates of the server # The key may be a file, or any URL supported by GnuTLS (e.g., # tpmkey:uuid=xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx;storage=user # or pkcs11:object=my-vpn-key;object-type=private) # # The server-cert file may contain a single certificate, or # a sorted certificate chain. # # There may be multiple server-cert and server-key directives, # but each key should correspond to the preceding certificate. # The certificate files will be reloaded when changed allowing for in-place # certificate renewal (they are checked and reloaded periodically; # a SIGHUP signal to main server will force reload). server-cert = /etc/ocserv/ssl/server-cert.pem server-key = /etc/ocserv/ssl/server-key.pem # Diffie-Hellman parameters. Only needed if you require support # for the DHE ciphersuites (by default this server supports ECDHE). # Can be generated using: # certtool --generate-dh-params --outfile /path/to/dh.pem #dh-params = /path/to/dh.pem # If you have a certificate from a CA that provides an OCSP # service you may provide a fresh OCSP status response within # the TLS handshake. That will prevent the client from connecting # independently on the OCSP server. # You can update this response periodically using: # ocsptool --ask --load-cert=your_cert --load-issuer=your_ca --outfile response # Make sure that you replace the following file in an atomic way. #ocsp-response = /path/to/ocsp.der # In case PKCS #11, TPM or encrypted keys are used the PINs should be available # in files. The srk-pin-file is applicable to TPM keys only, and is the # storage root key. #pin-file = /path/to/pin.txt #srk-pin-file = /path/to/srkpin.txt # The password or PIN needed to unlock the key in server-key file. # Only needed if the file is encrypted or a PKCS #11 object. This # is an alternative method to pin-file. #key-pin = 1234 # The SRK PIN for TPM. # This is an alternative method to srk-pin-file. #srk-pin = 1234 # The Certificate Authority that will be used to verify # client certificates (public keys) if certificate authentication # is set. ca-cert = /etc/ocserv/ssl/ca-cert.pem # The object identifier that will be used to read the user ID in the client # certificate. The object identifier should be part of the certificate's DN # Useful OIDs are: # CN = 2.5.4.3, UID = 0.9.2342.19200300.100.1.1 cert-user-oid = 0.9.2342.19200300.100.1.1 # The object identifier that will be used to read the user group in the # client certificate. The object identifier should be part of the certificate's # DN. Useful OIDs are: # OU (organizational unit) = 2.5.4.11 #cert-group-oid = 2.5.4.11 # The revocation list of the certificates issued by the 'ca-cert' above. # See the manual to generate an empty CRL initially. The CRL will be reloaded # periodically when ocserv detects a change in the file. To force a reload use # SIGHUP. #crl = /path/to/crl.pem # Uncomment this to enable compression negotiation (LZS, LZ4). compression = true # Set the minimum size under which a packet will not be compressed. # That is to allow low-latency for VoIP packets. The default size # is 256 bytes. Modify it if the clients typically use compression # as well of VoIP with codecs that exceed the default value. no-compress-limit = 256 # GnuTLS priority string; note that SSL 3.0 is disabled by default # as there are no openconnect (and possibly anyconnect clients) using # that protocol. The string below does not enforce perfect forward # secrecy, in order to be compatible with legacy clients. # # Note that the most performant ciphersuites are the moment are the ones # involving AES-GCM. These are very fast in x86 and x86-64 hardware, and # in addition require no padding, thus taking full advantage of the MTU. # For that to be taken advantage of, the openconnect client must be # used, and the server must be compiled against GnuTLS 3.2.7 or later. # Use "gnutls-cli --benchmark-tls-ciphers", to see the performance # difference with AES_128_CBC_SHA1 (the default for anyconnect clients) # in your system. #tls-priorities = "NORMAL:%SERVER_PRECEDENCE:%COMPAT:-VERS-SSL3.0" tls-priorities = "NORMAL:%SERVER_PRECEDENCE:%COMPAT:-VERS-SSL3.0" # More combinations in priority strings are available, check # http://gnutls.org/manual/html_node/Priority-Strings.html # E.g., the string below enforces perfect forward secrecy (PFS) # on the main channel. #tls-priorities = "NORMAL:%SERVER_PRECEDENCE:%COMPAT:-RSA:-VERS-SSL3.0:-ARCFOUR-128" # That option requires the established DTLS channel to use the same # cipher as the primary TLS channel. This cannot be combined with # listen-clear-file since the ciphersuite information is not available # in that configuration. Note also, that this option implies that # dtls-legacy option is false; this option cannot be enforced # in the legacy/compat protocol. #match-tls-dtls-ciphers = true # The time (in seconds) that a client is allowed to stay connected prior # to authentication auth-timeout = 240 # The time (in seconds) that a client is allowed to stay idle (no traffic) # before being disconnected. Unset to disable. idle-timeout = 1200 # The time (in seconds) that a client is allowed to stay connected # Unset to disable. #session-timeout = 86400 # The time (in seconds) that a mobile client is allowed to stay idle (no # traffic) before being disconnected. Unset to disable. mobile-idle-timeout = 1800 # The time (in seconds) that a client is not allowed to reconnect after # a failed authentication attempt. min-reauth-time = 3 # Banning clients in ocserv works with a point system. IP addresses # that get a score over that configured number are banned for # min-reauth-time seconds. By default a wrong password attempt is 10 points, # a KKDCP POST is 1 point, and a connection is 1 point. Note that # due to difference processes being involved the count of points # will not be real-time precise. # # Score banning cannot be reliably used when receiving proxied connections # locally from an HTTP server (i.e., when listen-clear-file is used). # # Set to zero to disable. max-ban-score = 50 # The time (in seconds) that all score kept for a client is reset. ban-reset-time = 300 # In case you'd like to change the default points. #ban-points-wrong-password = 10 #ban-points-connection = 1 #ban-points-kkdcp = 1 # Cookie timeout (in seconds) # Once a client is authenticated he's provided a cookie with # which he can reconnect. That cookie will be invalided if not # used within this timeout value. On a user disconnection, that # cookie will also be active for this time amount prior to be # invalid. That should allow a reasonable amount of time for roaming # between different networks. cookie-timeout = 300 # If this is enabled (not recommended) the cookies will stay # valid even after a user manually disconnects, and until they # expire. This may improve roaming with some broken clients. #persistent-cookies = true # Whether roaming is allowed, i.e., if true a cookie is # restricted to a single IP address and cannot be re-used # from a different IP. deny-roaming = false # ReKey time (in seconds) # ocserv will ask the client to refresh keys periodically once # this amount of seconds is elapsed. Set to zero to disable (note # that, some clients fail if rekey is disabled). rekey-time = 172800 # ReKey method # Valid options: ssl, new-tunnel # ssl: Will perform an efficient rehandshake on the channel allowing # a seamless connection during rekey. # new-tunnel: Will instruct the client to discard and re-establish the channel. # Use this option only if the connecting clients have issues with the ssl # option. rekey-method = ssl # Script to call when a client connects and obtains an IP. # The following parameters are passed on the environment. # REASON, USERNAME, GROUPNAME, HOSTNAME (the hostname selected by client), # DEVICE, IP_REAL (the real IP of the client), IP_REAL_LOCAL (the local # interface IP the client connected), IP_LOCAL (the local IP # in the P-t-P connection), IP_REMOTE (the VPN IP of the client), # IPV6_LOCAL (the IPv6 local address if there are both IPv4 and IPv6 # assigned), IPV6_REMOTE (the IPv6 remote address), IPV6_PREFIX, and # ID (a unique numeric ID); REASON may be "connect" or "disconnect". # In addition the following variables OCSERV_ROUTES (the applied routes for this # client), OCSERV_NO_ROUTES, OCSERV_DNS (the DNS servers for this client), # will contain a space separated list of routes or DNS servers. A version # of these variables with the 4 or 6 suffix will contain only the IPv4 or # IPv6 values. # The disconnect script will receive the additional values: STATS_BYTES_IN, # STATS_BYTES_OUT, STATS_DURATION that contain a 64-bit counter of the bytes # output from the tun device, and the duration of the session in seconds. #connect-script = /usr/bin/ocserv-script #disconnect-script = /usr/bin/ocserv-script # UTMP # Register the connected clients to utmp. This will allow viewing # the connected clients using the command 'who'. #use-utmp = true # Whether to enable support for the occtl tool (i.e., either through D-BUS, # or via a unix socket). use-occtl = true # PID file. It can be overriden in the command line. pid-file = /var/run/ocserv.pid # Set the protocol-defined priority (SO_PRIORITY) for packets to # be sent. That is a number from 0 to 6 with 0 being the lowest # priority. Alternatively this can be used to set the IP Type- # Of-Service, by setting it to a hexadecimal number (e.g., 0x20). # This can be set per user/group or globally. #net-priority = 3 # Set the VPN worker process into a specific cgroup. This is Linux # specific and can be set per user/group or globally. #cgroup = "cpuset,cpu:test" # # Network settings # # The name to use for the tun device device = vpns # Whether the generated IPs will be predictable, i.e., IP stays the # same for the same user when possible. predictable-ips = true # The default domain to be advertised default-domain = example.com # The pool of addresses that leases will be given from. If the leases # are given via Radius, or via the explicit-ip? per-user config option then # these network values should contain a network with at least a single # address that will remain under the full control of ocserv (that is # to be able to assign the local part of the tun device address). #ipv4-network = 192.168.1.0 #ipv4-netmask = 255.255.255.0 #ipv4-network = 10.10.0.0 #ipv4-netmask = 255.255.255.0 # An alternative way of specifying the network: ipv4-network = 192.168.1.0/24 # The IPv6 subnet that leases will be given from. #ipv6-network = fda9:4efe:7e3b:03ea::/64 # Specify the size of the network to provide to clients. It is # generally recommended to provide clients with a /64 network in # IPv6, but any subnet may be specified. To provide clients only # with a single IP use the prefix 128. #ipv6-subnet-prefix = 128 #ipv6-subnet-prefix = 64 # Whether to tunnel all DNS queries via the VPN. This is the default # when a default route is set. tunnel-all-dns = true # The advertized DNS server. Use multiple lines for # multiple servers. # dns = fc00::4be0 # dns = 192.168.1.2 # dns = 8.8.8.8 # dns = 8.8.4.4 dns = 1.1.1.1 dns = 1.0.0.1 # The NBNS server (if any) #nbns = 192.168.1.3 # The domains over which the provided DNS should be used. Use # multiple lines for multiple domains. #split-dns = example.com # Prior to leasing any IP from the pool ping it to verify that # it is not in use by another (unrelated to this server) host. # Only set to true, if there can be occupied addresses in the # IP range for leases. ping-leases = false # Use this option to enforce an MTU value to the incoming # connections. Unset to use the default MTU of the TUN device. #mtu = 1420 # Unset to enable bandwidth restrictions (in bytes/sec). The # setting here is global, but can also be set per user or per group. #rx-data-per-sec = 40000 #tx-data-per-sec = 40000 # The number of packets (of MTU size) that are available in # the output buffer. The default is low to improve latency. # Setting it higher will improve throughput. #output-buffer = 10 # Routes to be forwarded to the client. If you need the # client to forward routes to the server, you may use the # config-per-user/group or even connect and disconnect scripts. # # To set the server as the default gateway for the client just # comment out all routes from the server, or use the special keyword # 'default'. #route = 10.10.10.0/255.255.255.0 #route = 192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0 #route = fef4:db8:1000:1001::/64 # Subsets of the routes above that will not be routed by # the server. #no-route = 192.168.5.0/255.255.255.0 # If set, the script /usr/bin/ocserv-fw will be called to restrict # the user to its allowed routes and prevent him from accessing # any other routes. In case of defaultroute, the no-routes are restricted. # All the routes applied by ocserv can be reverted using /usr/bin/ocserv-fw # --removeall. This option can be set globally or in the per-user configuration. #restrict-user-to-routes = true # When set to true, all client's iroutes are made visible to all # connecting clients except for the ones offering them. This option # only makes sense if config-per-user is set. #expose-iroutes = true # Groups that a client is allowed to select from. # A client may belong in multiple groups, and in certain use-cases # it is needed to switch between them. For these cases the client can # select prior to authentication. Add multiple entries for multiple groups. # The group may be followed by a user-friendly name in brackets. #select-group = group1 #select-group = group2[My special group] # The name of the (virtual) group that if selected it would assign the user # to its default group. #default-select-group = DEFAULT # Instead of specifying manually all the allowed groups, you may instruct # ocserv to scan all available groups and include the full list. #auto-select-group = true # Configuration files that will be applied per user connection or # per group. Each file name on these directories must match the username # or the groupname. # The options allowed in the configuration files are dns, nbns, # ipv?-network, ipv4-netmask, rx/tx-per-sec, iroute, route, no-route, # explicit-ipv4, explicit-ipv6, net-priority, deny-roaming, no-udp, # user-profile, cgroup, stats-report-time, and session-timeout. # # Note that the 'iroute' option allows to add routes on the server # based on a user or group. The syntax depends on the input accepted # by the commands route-add-cmd and route-del-cmd (see below). The no-udp # is a boolean option (e.g., no-udp = true), and will prevent a UDP session # for that specific user or group. #config-per-user = /etc/ocserv/config-per-user/ #config-per-group = /etc/ocserv/config-per-group/ # When config-per-xxx is specified and there is no group or user that # matches, then utilize the following configuration. #default-user-config = /etc/ocserv/defaults/user.conf #default-group-config = /etc/ocserv/defaults/group.conf # The system command to use to setup a route. %{R} will be replaced with the # route/mask and %{D} with the (tun) device. # # The following example is from linux systems. %R should be something # like 192.168.2.0/24 (the argument of iroute). #route-add-cmd = "ip route add %{R} dev %{D}" #route-del-cmd = "ip route delete %{R} dev %{D}" # This option allows to forward a proxy. The special keywords '%{U}' # and '%{G}', if present will be replaced by the username and group name. #proxy-url = http://example.com/ #proxy-url = http://example.com/%{U}/ # This option allows you to specify a URL location where a client can # post using MS-KKDCP, and the message will be forwarded to the provided # KDC server. That is a translation URL between HTTP and Kerberos. # In MIT kerberos you'll need to add in realms: # EXAMPLE.COM = { # kdc = https://ocserv.example.com/kerberos # http_anchors = FILE:/etc/ocserv-ca.pem # } # This option is available if ocserv is compiled with GSSAPI support. #kkdcp = SERVER-PATH KERBEROS-REALM PROTOCOL@SERVER:PORT #kkdcp = /kerberos EXAMPLE.COM udp@127.0.0.1:88 #kkdcp = /kerberos-tcp EXAMPLE.COM tcp@127.0.0.1:88 # # The following options are for (experimental) AnyConnect client # compatibility. # This option will enable the pre-draft-DTLS version of DTLS, and # will not require clients to present their certificate on every TLS # connection. It must be set to true to support legacy CISCO clients # and openconnect clients < 7.08. When set to true, it implies dtls-legacy = true. cisco-client-compat = true # This option allows to disable the DTLS-PSK negotiation (enabled by default). # The DTLS-PSK negotiation was introduced in ocserv 0.11.5 to deprecate # the pre-draft-DTLS negotiation inherited from AnyConnect. It allows the # DTLS channel to negotiate its ciphers and the DTLS protocol version. #dtls-psk = false # This option allows to disable the legacy DTLS negotiation (enabled by default, # but that may change in the future). # The legacy DTLS uses a pre-draft version of the DTLS protocol and was # from AnyConnect protocol. It has several limitations, that are addressed # by the dtls-psk protocol supported by openconnect 7.08+. dtls-legacy = true # Client profile xml. A sample file exists in doc/profile.xml. # It is required by some of the CISCO clients. # This file must be accessible from inside the worker's chroot. user-profile = profile.xml #Advanced options # Option to allow sending arbitrary custom headers to the client after # authentication and prior to VPN tunnel establishment. You shouldn't # need to use this option normally; if you do and you think that # this may help others, please send your settings and reason to # the openconnect mailing list. The special keywords '%{U}' # and '%{G}', if present will be replaced by the username and group name. #custom-header = "X-My-Header: hi there"
- На этом с конфигурационным файлом мы закончили. Нужно включить маршрутизацию в системе. Для этого в файле /etc/sysctl.conf добавляем одну строчку.
# net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
Перечитываем изменения.
# sysctl -p
Создание пользователей в OpenConnect Vpn
- В конфигурационном файле сервера, мы настроили аутентификацию по логину и паролю. Кроме того, мы указали файл в котором будут находится эти данные. Пришло время создать данный файл.
# touch /etc/ocserv/passwd
- Файл готов, и теперь можно создать первого пользователя.
- Для примера я создам пользователя user в группе default.
# ocpasswd -c /etc/ocserv/passwd -g default user
- Пользователю необходимо будет создать пароль.

- Со стороны сервера, все настройки закончены. Можно запускать сервер, и добавлять его в автозагрузку.
# systemctl start ocserv # systemctl enable ocserv
- Проверяем статус OpenConnect сервера.
# systemctl status ocserv
Настройка Firewall для работы OpenConnect сервера
- Если всё в норме, то можно переходить к последнему шагу, настройке Firewall.
- Вот команды для iptables. Во втором правиле, не забудьте указать ip-адрес Вашего сервера
# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT # iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source ip_адрес_сервера # iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A FORWARD -p all -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # /sbin/iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
- А можно запустить скрипт с этими правилами, и дополнительными настройками. Не забудьте указать IP_АДРЕС_ВАШЕГО_СЕРВЕРА.
#!/bin/sh export IF_EXT="eth0" export IPT="/sbin/iptables" export IPT6="/sbin/ip6tables" # Очистка всех цепочек iptables $IPT -F $IPT -F -t nat $IPT -F -t mangle $IPT -X $IPT -t nat -X $IPT -t mangle -X $IPT6 --flush # loopback $IPT -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT $IPT -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT # default $IPT -P INPUT DROP $IPT -P OUTPUT DROP $IPT -P FORWARD DROP $IPT6 -P INPUT DROP $IPT6 -P OUTPUT DROP $IPT6 -P FORWARD DROP # allow forwarding echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward # NAT # ######################################### # SNAT - local users to out internet $IPT -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source IP_АДРЕС_ВАШЕГО_СЕРВЕРА $IPT -I FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --clamp-mss-to-pmtu $IPT -A INPUT -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP $IPT -A OUTPUT -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP # INPUT chain # ######################################### $IPT -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP $IPT -A FORWARD -m state --state INVALID -j DROP $IPT -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP $IPT -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT $IPT -A INPUT -i $IF_EXT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT $IPT -A INPUT -i $IF_EXT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT # FORWARD chain # ######################################### $IPT -A FORWARD -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT $IPT -A FORWARD -p all -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # OUTPUT chain # ######################################### $IPT -A OUTPUT -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # Записываем правила /sbin/iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
- Перезапускаем iptables.
# systemctl restart iptables
- Вот команды для firewalld:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=443/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-masquerade
- Перезапускаем firewalld:
# systemctl reload firewalld
Подключение к OpenConnect серверу при помощи клиентского приложения
- Пришло время пробовать подключиться к OpenConnect серверу клиентским приложением.
- Я буду производить подключение в ОС Windows.
- Запускаем программу, жмём на шестерёнку, и выбираем «New profile».
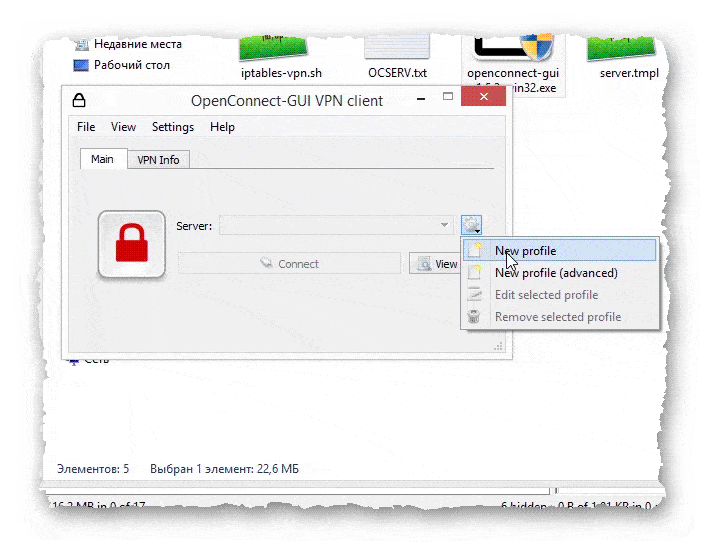
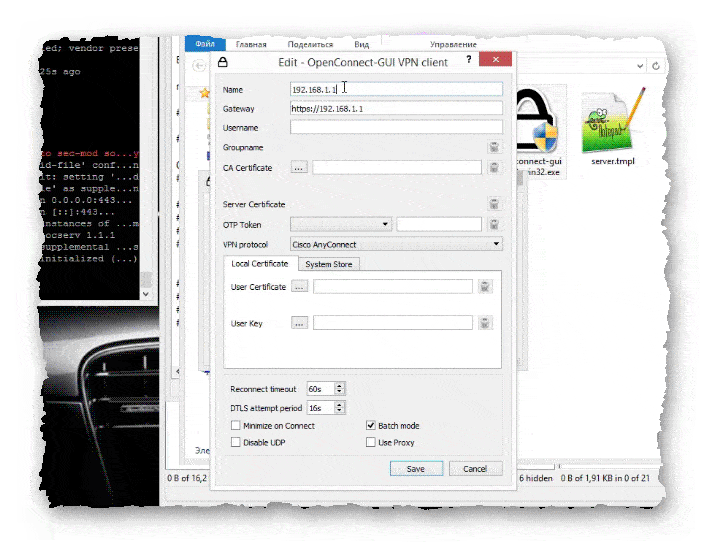
- Открывается окно для ввода данных сервера, к которому нужно подключиться.
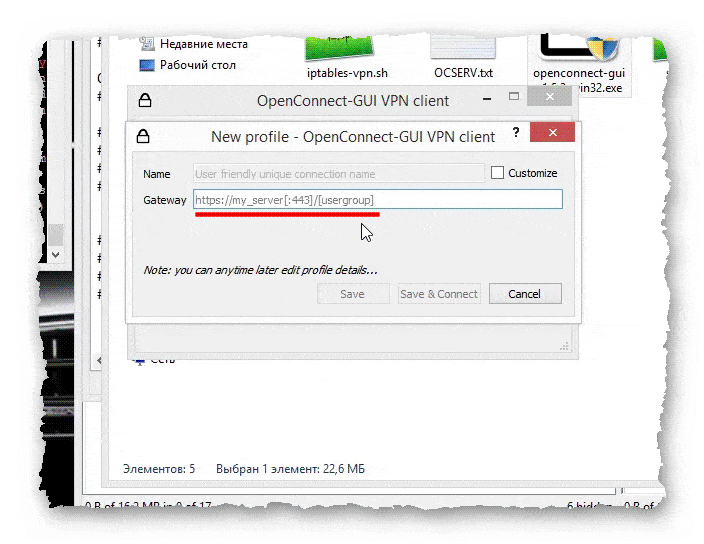
- После ввода необходимых данных, становятся активными кнопки «Save» и «Save & Connect».
- Если нажать на «Save», то профиль подключения будет просто сохранён. При нажатии на вторую кнопку - будет произведено сохранение профиля, и подключение к желаемому серверу.
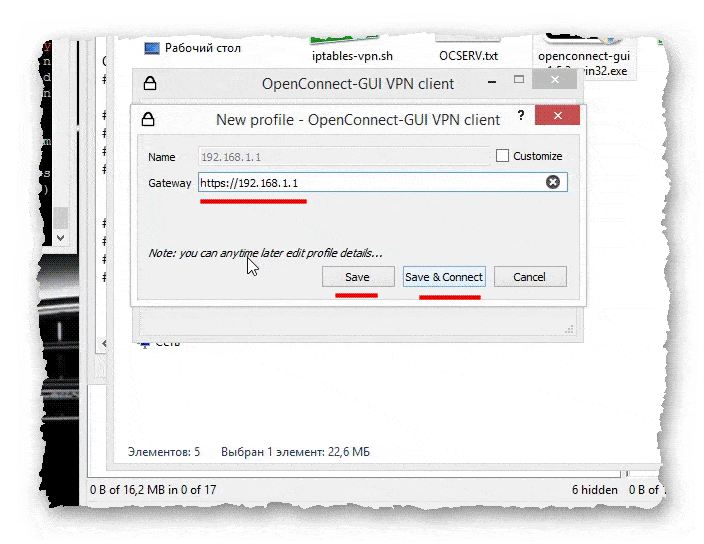
- Зайдя в редактирование профиля, можно изменить параметры профиля на своё усмотрение.
- При подключении к серверу, нужно будет вводить данные: пользователь и пароль.
- Если всё сделано правильно, и произошло подключение к удалённому серверу OpenConnect, то окно программы меняется на режим «Connect».

Сегодня мы рассмотрели тему: "Установка OpenConnect сервера в СentOS 7". Установили и настроили сервер, а так же произвели подключение программой клиентом. Смотрите так же видео по теме.
Надеюсь статья была вам полезна. До встречи в новых статьях.
✍
С уважением, Андрей Бондаренко.
Видео на тему "Установка OpenConnect сервера в СentOS 7":

WMZ-кошелёк = Z667041230317
«Linux»

Arsen
Здравствуйте, если у Вас есть время и возможность, Вы не могли бы мне помочь. Я все делаю как написано, но у меня проблема начинается на этом месте ipv4-network = 192.168.1.0/24 и дальше с портами. Пожалуйста помогите
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте.
А что не так с ipv4-network = 192.168.1.0/24?
Нужно найти данную строчку, и убрать перед ней # решётку. Если строчки нет, то нужно её добавить.
Какие порты?
Если порты для работы ocserv, то по умолчанию сервер работает на 443 портах tcp и udp, можете оставить как есть, но тогда нужно будет дополнительно открывать 443 udp-port в Firewall, либо удалите строчку udp-port = 443 в конфигурационном файле, как написано в статье.
Если Вы о портах в Firewall, то в статье указывается настройка для iptables.
Установите iptables https://aeb-blog.ru/linux/ustanovka-utility-iptables-v-centos/
Либо добавьте правила в firewalld:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=443/tcp# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-masquerade
# systemctl reload firewalld
Kerim
Здравствуйте уважаемый Андрей Бондаренко, если можете помогите пожалуйста, у меня такая проблема: сервер я настроил, подключается без проблем, но как я подключусь к серверу то режется скорость интернета, очень медленно начинает работать интернет, что можно сделать в данной ситуации? Заранее большое спасибо.
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте, уважаемый Керим!
По Вашему вопросу:
Если Вы производили настройку без ошибок, и точно по этой статье, то проблема со скоростью, не в конфигурации сервера.
Во-первых, скорость может зависеть от того, на каком удалении физически расположен Ваш сервер. Проверьте скорость до Вашего сервера.
Во-вторых, узнайте какую реально пропускную способность предоставляет Ваш хостинг-провайдер.
Вот полезная ссылка на статью, как реализовать проверку до сервера, и от сервера дальше:
—————-
https://www.reg.ru/support/vydelennyye-servery-i-dts/dedicated/reshenie-problem-pri-rabote-s-dedicated/kak-uznat-skorost-soyedineniya-vydelennyye-servera-s-internetom
—————-
В-третьих, некоторые хостинг-провайдеры, ближе к ночи, сами режут скорость (моё личное наблюдение), возможно в целях экономии.
В-четвёртых, возможно какие-то фильтры у Вашего интернет провайдера.
—————-
Попробуйте изменить dns в конфиге на 1.1.1.1 и 1.0.0.1, они пошустрее.
Для стабильности соединения, попробуйте вот это:
https://aeb-blog.ru/linux/nastrojka-tcp-bbr-ot-google-v-centos-7/
Kollos
Доброго Вам времени суток Андрей Бондаренко. Скажите пожалуйста есть ли возможность изменить шифрование ECDHE_RSA_AES128_GCM__SHA256 на ECDHE_RSA_AES256_GCM_SHA384, если есть, то скажите пожалуйста как!?
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте!
Я чесно говоря не вдавался в такие подробности.
Меня Openconnect больше интересовал со стороны своей незаметности, и идентичности обычному HTTPS трафику. В связи с чем, не особой заметности в общем потоке трафика. Для навороченного шифрования, есть например openvpn.
Ну а если есть такая надобность, чтобы подкрутить шифрование на Openconnect, то в конфигурационном файле ocserv.conf (строчка 261), описывается возможность настройки ciphers:
gnutls-cli --benchmark-tls-ciphersВот например статья на github, в которой в частности, процесс настройки наборов шрифтов рассматривается по подробней:
—————————————————————————
https://github.com/hardenedlinux/Debian-GNU-Linux-Profiles/blob/master/docs/tls/openconnect-server-ocserv-on-debian.md
—————————————————————————
Валерий
Здравствуйте. Помогите пожалуйста! У меня не запускается сервер :
ocserv.service — OpenConnect SSL VPN server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ocserv.service; enabled; vendor prese t: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Tue 2021-05-11 11:12:54 MSK; 27s ago
Docs: man:ocserv(8)
Process: 1755 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/ocserv —pid-file /var/run/ocserv.pid —conf ig /etc/ocserv/ocserv.conf -f (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Process: 1754 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/ocserv-genkey (code=exited, status=0/SUCC ESS)
Main PID: 1755 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru systemd[1]: Starting O…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru systemd[1]: Started Op…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru ocserv[1755]: note: sk…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru ocserv[1755]: error: c…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru ocserv[1755]: note: vh…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru systemd[1]: ocserv.ser…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru systemd[1]: Unit ocser…
May 11 11:12:54 194-58-97-123.cloudvps.regruhosting.ru systemd[1]: ocserv.ser…
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте!
То что Вы выложили, не о чём не говорит.
Нужно выполнить команду:
#
systemctl status ocserv -lА лучше заглянуть в системный лог, если у Вас CentOS 7, то это /var/log/messages.
Проблема может быть в неправильных настройках конфигурационного файла ocserv.conf, либо в его отсутствии вообще.
Валерий
Сделал все по инструкции. Ошибка началась с раздела: Настройка Firewall для работы OpenConnect сервера. Я занес в терминале:
# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp —dport 443 -m state —state NEW -j ACCEPT
# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j SNAT —to-source ip_адрес_сервера
# iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A FORWARD -p all -m state —state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# /sbin/iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables <вот это не получилось внести.
Пробовал сохранить скрипт на сервере с помощью WinSCP, как показано на вашем видео, но почему-то у меня нет прав на внесение изменений в любой из директорий.
Андрей Бондаренко
Что у Вас установлено и работает, firewalld или iptables?
И работает ли у ВАС, что-нибудь из этого вообще?
Firewalld и Iptables, это инструменты для управления системным Firewall. В системе используется либо одна утилита, либо другая.
В зависимости от использования firewalld или iptables, команды для настройки системного Firewall, соответственно отличаются.
Судя по Вашему комментарию, либо работает firewalld, либо вообще ничего.
Сначала проверьте, что у Вас работает:
# systemctl status firewalld# systemctl status iptables
Если ничего не работает, то нужно установить, запустить, и добавить в автозагрузку:
Для iptables:
# yum -y install iptables-services# systemctl start iptables.service
# systemctl enable iptables.service
Для firewalld:
# yum -y install firewalld# systemctl start firewalld
# systemctl enable firewalld
Для настройки с помощью firewalld, нужно выполнить:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=443/tcp# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-masquerade
# systemctl reload firewalld
Для настройки с помощью iptables, нужно выполнить то, что написано в статье.
Насчёт отсутствия прав в любой директории:
После добавления скрипта на сервер, нужно зайти в его свойства, и изменить chmod на 0740.
Ali
Dobry den. skazhite pozhalusta a kak podklyuchit na iphone openconnect
Андрей Бондаренко
Добрый день.
Приложение Cisco AnyConnect, вот ссылка в App Store:
———————
https://apps.apple.com/ru/app/cisco-anyconnect/id1135064690
———————
Ali
Spasibo za otwet. Skazhite pozhalusta mozhno udalit usera i mozhnoli posmotret spisok userow? Yesli mozhno skazhite pozhalusta kak eto zdelat
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте!
Список пользователей находится в файле, в который Вы их заносите:
# ocpasswd -c /etc/ocserv/passwd -g default user
Ну и удалять соответственно, нужно из этого файла.
Дмитрий
здравствуйте Андрей Бондаренко! делал все по инструкции проблемы начались с редактированием sysctl.conf он выглядит по другому
# sysctl settings are defined through files in
# /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/, and /etc/sysctl.d/.
#
# Vendors settings live in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/.
# To override a whole file, create a new file with the same in
# /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. To override
# only specific settings, add a file with a lexically later
# name in /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there.
#
# For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5).
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте, Дмитрий!
Не Важно как выглядит этот файл. Содержимое файла, зависит от версии ОС, и предустановок сделанных хостинг-провайдером.
Вам нужно включить маршрутизацию в системе. Для этого нужно добавить в этот файл:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
Дмитрий
спасибо за ответ.
Да я сделал это .после добавил пользователя и запустил сервер при проверки статуса выдает
● ocserv.service — OpenConnect SSL VPN server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ocserv.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Sat 2021-06-05 12:00:42 CEST; 18s ago
Docs: man:ocserv(8)
Main PID: 2542 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com systemd[1]: Starting OpenConn…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com systemd[1]: Started OpenConne…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com ocserv[2542]: note: skipping …
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com ocserv[2542]: error: cannot o…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com ocserv[2542]: error: cannot o…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com ocserv[2542]: error: the ‘aut…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com systemd[1]: ocserv.service: m…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com systemd[1]: Unit ocserv.servi…
Jun 05 12:00:42 dmitriynesterenko88.example.com systemd[1]: ocserv.service fa…
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
что не так подскажите пожалуйста.
Андрей Бондаренко
Скорее всего ошибка в конфиге ocserv.conf.
Смотрите логи в /var/log/messages.
Дмитрий
Здравствуйте Андрей!помогите в таком вопросе.
Как пустить весь трафик через UDP протокол?
Пробовал удалять Tcp 443 в файле ocserver он просто перестаёт запускаться
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте, Дмитрий!
Нужно было почитать документацию:
Сервер поддерживает два соединения/канала с клиентом. Основной канал VPN устанавливается через TCP, HTTP и TLS. Это канал управления, а также резервный канал данных. После его создания инициируется канал UDP с использованием DTLS, который служит основным каналом данных. Если канал UDP не устанавливается или временно недоступен, используется резервный канал через TCP/TLS.
Из выше написанного следует, что OpenConnect может работать без использования UDP, но без TCP никак…
Дмитрий
Он работает запускается но через TCP медленный хотелось чтобы трафик шёл через udp чтобы чуточку шустрее был
Андрей Бондаренко
По UDP сервер не будет работать, я уже объяснил Вам в предыдущем комментарии.
— Проблема со скоростью, может быть из-за неправильной конфигурации. Я добавил в статью готовый конфигурационный файл (сравните со своими настройками), который использовал лично не менее 10 раз. При этом никаких проблем со скоростью не было.
— Проблемы бывают при использовании графического клиента под Windows, это бета версия, и у меня например постоянно вылетала. На Linux и на мобильных, никогда проблем не было.
Дмитрий Нест
Здравствуйте Андрей. С наступающим новым годом!!!
подскажите можно ли создать нового пользователя на определенный срок?
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте. И Вас с наступающим новым годом!
1. Можно настроить аутентификацию по сертификату, а сертификат выписывать на определённый срок.
2. Можно при необходимости вручную удалять пользователя по истечении определённого срока.
Ali
Brat sozdat pozhalusta kontent pro wireguard. W internete mnogo informasiya pro wireguarda no yest odin no. Zdelayesh wsyo instruksii podklucheniya k wireguard yest no internet netu. 70% U lyudey takayezhe problema. A w internete net resheniya etoy problemu
Андрей Бондаренко
Если есть подключение и нет интернета, значит не активирован IP-маскарад на интерфейсе, или не активирована маршрутизация в системе.
Ali
Zdrawstwuyte. ya kupil vps inz yandex clouda. izdelal wsyo po instruksii. seyidineniya yest no netu internet. Pomogite pozhalusta. tam yest i wneshny IP i wnutrenny Ip
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте.
Либо не включена маршрутизация в /etc/sysctl.conf, либо ошибка в настройке системного Firewall.
Если конечно нет проблем на стороне хостинга.
Ali
Brat sozday pozhalusta kontent pro kak ustanowit openconnect na ubuntu 20.04.
Андрей Бондаренко
Принцип в целом одинаковый.
Serdar
Привет! мне нужен помош
Андрей Бондаренко
Привет. Чем могу помочь?
Han
Dobry den. Ya nastroil vpn wyo ok. Status ocserv aktiven, i firewall tozhe nastroil aktiven, no pri podklyucheniye posle wwedeniye parolya sbarywayet. Pomogite yesli mozhno. Wot log fail:
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | POST https://X.X.X.X/
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | Attempting to connect to server X.X.X.X:443
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | Connected to X.X.X.X:443
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | There was a non-CA certificate in the trusted list: OU=Copyright (c) 1997 Microsoft Corp.,OU=Microsoft Corporation,CN=Microsoft Root Authority.
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | There was a non-CA certificate in the trusted list: C=US,O=MSFT,CN=Microsoft Authenticode(tm) Root Authority.
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | There was a non-CA certificate in the trusted list: CN=Root Agency.
2023-01-24 11:27:47 | 44cc | SSL negotiation with X.X.X.X
2023-01-24 11:27:48 | 44cc | Server certificate verify failed: signer not found
2023-01-24 11:27:48 | 44cc | Connected to HTTPS on X.X.X.X
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Got HTTP response: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpncontext=; expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 22:00:00 GMT; path=/; Secure
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Content-Type: text/xml
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Content-Length: 306
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | X-Transcend-Version: 1
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | HTTP body length: (306)
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | XML POST enabled
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Please enter your username.
2023-01-24 11:27:49 | 44cc | Text form: username
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | POST https://X.X.X.X/auth
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Got HTTP response: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpncontext=ABAw8CC77UeVPfmxT6xx9psZHp1b3ixpKTyt8os0ZwE=; Max-Age=300; Secure
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Content-Type: text/xml
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Content-Length: 310
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | X-Transcend-Version: 1
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | HTTP body length: (310)
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Please enter your password.
2023-01-24 11:28:00 | 44cc | Password form: password
2023-01-24 11:28:04 | 44cc | POST https://X.X.X.X/auth
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Got HTTP response: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Connection: Keep-Alive
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Content-Type: text/xml
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Content-Length: 446
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | X-Transcend-Version: 1
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpncontext=ABAw8CC77UeVPfmxT6xx9psZHp1b3ixpKTyt8os0ZwE=; Secure
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpn=; Secure
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpnc=; expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 22:00:00 GMT; path=/; Secure
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Set-Cookie: webvpnc=bu:/&p:t&iu:1/&sh:1F016EE3873A115404C2DAE45154182543150F31&lu:/+CSCOT+/translation-table?textdomain%3DAnyConnect%26type%3Dmanifest&fu:profiles
Fprofile.xml&fh:A8B0B07FBA93D06E8501E40AB807AEE2464E73B7; path=/; Secure
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | HTTP body length: (446)
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Got inappropriate HTTP CONNECT response: HTTP/1.1 401 Cookie is not acceptable
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 44cc | Error establishing the CSTP channel
2023-01-24 11:28:05 | 3a60 | Disconnected
Андрей Бондаренко
Здравствуйте.
Может поможет:
https://github.com/StreisandEffect/streisand/issues/1546